Download ECGs, Illustrations, and other Resources for your classes.
ALL OUR CONTENT IS FREE OF CHARGE AND FREE OF COPYRIGHT IF USED IN A CLASSROOM SETTING
ECG Challenge from
Limmer Creative & ECG Guru
ECG & ILLUSTRATIONS ARCHIVES SEARCH (SCROLLABLE LIST)
- 12 channel ECG
- 12-Lead and Rhythm Strip
- 15-Lead ECG
- 2:1 conducton
- A Fib
- ACS
- AIVR
- APB
- ATP
- AV dissociation
- AV Block
- AV Reentry Tachycardia
- AV block and ST elevation
- AV blocks
- AV dissociation
- AV nodal reentry tachycardia
- AV nodal rhythm
- AVNRT
- AVRT
- AWMI
- Aberrant conduction
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
- Accessory pathway
- Accessory pathway conduction illustration
- Acidosis
- Acute M.I.
- Adenosine
- Agonal rhythm
- Akinesis
- Amyloidosis
- Angiogram
- Angioplasty
- Anterior M.I.
- Anterior wall M.I
- Anterior wall M.I.
- Anterior-lateral M.I.
- Anterior-lateral M.I.
- Anterior-lateral M.I.
- Anterior-septal M.I.
- Anti-tachycardia
- Anti-tachycardia pacing
- Antitachycardia pacing
- Aortic stenosis
- Apical ballooning syndrome
- Arm lead reversal
- Artifact
- Atrial abnormality
- Atrial bigeminy
- Atrial echo beat
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
- Atrial flutter
- Atrial flutter with ariable conduction
- Atrial fusion
- Atrial pacemaker
- Atrial premature beat
- Atrial tachycardia
- Atrial trigeminy
- Atrio-ventricular blocks
- Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia
- Atypical atrial flutter
- Axis
- Axis deviation
- Axis shift
- BER
- Basic ECG
- Basic rhythm strip
- Benign early repolarization
- Bi-atrial enlargement
- Bifascicular block
- Bigeminy
- Biventricular pacemaker
- Blank ECG paper
- Blocked PACs
- Blog post
- Bradycardia - Tachycardia Syndrome
- Bradycardia
- Brugada
- Brugada Syndrome
- Brugada pattern
- Brugada sign
- Bundle branch block
- CAD
- COPD
- Cabrera format
- Cabrera or Panoramic format
- Capture beats
- Cardiac arrest
- Cardiac memory
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy
- Cardiogenic shock
- Cardioversion
- Cath lab images
- Central nervous system disorder
- Channelopathy
- Chest leads
- Circumflex artery
- Circumflex artery occlusion
- Circumflex artery occlustion
- Circumflex occlusion
- Colateral circulation
- Concealed P waves
- Concealed conduction
- Concealed retrograde conduction
- Conduction system
- Congestive cardiomyopathy
- Conversion of PSVT
- Coronary arteries
- Coronary artery disease
- Coronary artery spasm
- Coronary syndrome
- Couplets
- Coupling interval
- DECREMENTAL CONDUCTION
- DKA
- DSI
- Defibrillation
- Delta wave
- Delta waves
- Dextrocardia
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Diffuse ischemia
- Diffuse subendocardial ischemia
- Digitalis Toxicity
- Dominant circumflex artery
- Dominant left circumflex
- Double tachycardia
- Dr. Andreas Roeschl
- Dr. Jerry W Jones
- Dual A-V nodal conduction
- Dual AV conduction pathways
- Dual AV pathways
- ECG Basics
- ECG Book
- ECG Challenge
- ECG misdiagnosis by machine
- ECG teaching series
- Early Repolarization
- Einthoven’s triangle illustration
- Electrical alternans
- Electrode switching
- Electrolyte effects
- Electronic Wenckebach
- Escape rhythm
- Escape-capture bigeminy
- Fascicular VT
- Fascicular block
- Fascicular tachycardia
- Floating P-R interval
- Fusion beat
- Fusion beats
- Giant T waves
- Global ischemia
- Glossary
- Grouped beating
- Guillain-Barre' Syndrome
- Hemiblock
- High grade AV block
- High-grade AV Block
- Holter monitor
- Hyperacute T waves
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypertension
- Hypervagotonia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypothermia
- ICD
- II
- IPWMI
- IVCD
- IWMI
- Idiojunctional escape rhythm
- Idiojunctional rhythm
- Idiojunctional tachycardia
- Idiopathic ventricular tachycardia
- Idioventricular escape rhythm
- Idioventricular rhythm
- Illlustration Precordial leads
- Illustration
- Illustration V4Right Placement
- Illustration posterior leads
- Illustration: Cardiac Conduction System
- Illustration: Determining Rate
- Illustration: Pacemaker leads
- Illustration: Accessory pathway
- Illustration: Angiogram of non-dominant right coronary artery
- Illustration: Anterior-septal M.I.
- Illustration: Benign early repolarization
- Illustration: Bi-ventricular pacemaker
- Illustration: Blank ECG paper
- Illustration: Complete heart block
- Illustration: Dominant circumflex artery
- Illustration: Dominant left circumflex
- Illustration: Dominant left circumflex artery labelled; Dominant left circumflex artery
- Illustration: Dual chamber pacemaker
- Illustration: Einthoven's Triangle
- Illustration: Interior view of heart
- Illustration: Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Illustration: Lewis lead
- Illustration: Reentry Mechanism
- Illustration: Right chest leads
- Illustration: Standard Leads I
- Illustration: Two types of complete heart block
- Illustration: U Waves
- Illustration: V4Right Placement
- Illustration: Ventricular systole
- Illustration: angiogram
- Illustration: heart anatomy
- Impending trifacicular AVB
- Impending ventricular standstill
- Incomplete right bundle branch block
- Incorrect machine interpretation
- Inferior M.I.
- Inferior Wall
- Inferior Wall M.I.
- Inferior-lateral M.I.
- Inferior-posterior M.I.
- Inferoposterior M.I.
- Intermittent atrial fibrillation
- Intermittent bundle branch block
- Intermittent trifascicular block
- Interpolated VPB
- Interventricular conduction defect
- Interventricular conduction delay
- Intraatrial block
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Intraventricular conduction delay
- Inverted P waves
- Ischemia
- Isolated posterior wall M.I.
- Isorhythmic A-V dissociation
- Jerry W Jones
- Junctional
- Junctional escape
- Junctional rhythm
- Kent Bundle
- LBBB
- LBBB Left bundle branch block
- LQTS
- Labelled ventriculogram
- Laddergram
- Lateral M.I.
- Lateral wall M.I.
- Lead I sign
- Lead reversal
- Left atrial abnormality
- Left atrial enlargement
- Left bundle branch block
- Left bundle branch block with acute M.I.
- Left main coronary artery obstruction
- Left main coronary artery occlusion
- Left ventricular enlargement
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Lewis lead
- Long PR interval
- Long QT
- Long QT Syndrome
- Long QT interval
- Loose electrode artifact
- Low atrial rhythm
- Low voltage QRS
- Lyme disease
- M.I. with non-obstructive coronary arteries
- MAT
- MINOCA
- Masquerading bundle branch block
- Mirror-image dextrocardia
- Mobitz I
- Mobitz I AV block
- Mobitz I block
- Mobitz II AV block
- Multi-lead assessment
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia
- Multilevel AV block
- Myocardial infarction
- Myopathy
- NIPS Procedure
- NSTEMI
- Narrow-complex tachycardia
- Non-STEMI
- Non-conducted P waves
- Non-conducted PAC
- Non-conducted PACs
- Non-conducted premature atrial contractions
- Non-respiratory sinus arrhythmia
- Non-specific intraventricular conduction delay
- Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia
- Normal 12-lead ECG
- Normal
- Normal rhythm
- Normal variants
- OMI
- Obtuse marginal artery
- Occlusion M.I.
- Occlusion myocardial infarction
- Occlusive myocardial infarction
- Orthotopic heart transplant
- Osborn waves
- Overdrive pacing
- Overdrive suppression
- P mitrale
- P pulmonale
- PAC
- PAC with aberrant conduction
- PACs
- PR alternans
- PR depression
- PR segment
- PSVT
- PVC
- PVC with VA conduction
- PVCs
- Paced pseudofusion
- Pacemaker
- Pacemaker illustration
- Pacemaker wire pseudo malplacement
- Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
- Pathological Q waves
- Peaked T waves
- Pediatric ECG
- Pericardial effusion
- Pericarditis
- Philadelphia clue
- Physiological block
- Polymorphic VT
- Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
- Poor R wave progression
- Posterior M.I
- Posterior M.I.
- Posterior leads illustration
- Posterior wall M.I.
- Pre-automatic pause
- Pre-excitation
- Precordial concordance
- Preexcitation
- Prematur eventricular contractions
- Premature atrial contraction
- Premature atrial contractions
- Premature junctional contraction
- Premature ventricular contraction
- Premature ventricular contractions
- Previous M.I.
- Prolonged PR interval
- Prolonged QT interval
- Prolonged QTc interval
- Proximal LAD occlusion
- Proximal LCA
- Proximal occlusion of LAD
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Pulseless electrical activity
- Q waves
- QRS fragmentation
- R wave morphology
- R wave progression
- R-P / P-R reciprocity
- R-P/P-R reciprocity
- RBBB
- RBBB and LAFB
- RRWCT
- RVOT
- Rabbit-ear sign
- Rapid ventricular response
- Rate-related LBBB
- Rate-related bundle branch block
- Reciprocal ST changes
- Reciprocal ST depression
- Reciprocal changes
- Reciprocating tachycardia
- Refractory period
- Refractory periods
- Regular really wide complex tachycardia
- Renal failure
- Reperfusion
- Repolarization abnormalities
- Respiratory sinus arrhythmia
- Retrograde P waves
- Retrograde atrial activation
- Retrograde concealed conduction
- Retrograde conduction
- Reversed arm cables
- Reversed reciprocal beat
- Rhythm strip
- Right bundle branch block
- Right coronary artery
- Right coronary artery occlusion
- Right ventricular M.I.
- Right ventricular enlargement
- Right ventricular outflow tract tachycardia
- Right-sided series
- SA block
- SA block Type II
- SA exit block
- SSS
- ST and T wave changes
- ST changes
- ST depression
- ST elevation
- ST elevation in aVR
- SVT
- Schamroth's sign
- Second-degree AV block
- Second-degree AVB Type I
- Secondary ST changes
- Sgarbossa criteria
- Sgarbossa's Criteria
- Sharks fin pattern
- Sick sinus syndrome
- Sick-sinus syndrome
- Sine wave
- Sino-atrial exit block
- Sinus node dysfunction
- Sinus rhythm
- Situs inversus
- Slurring at base of R wave
- Smith Modified Sgarbossa Criteria
- Smith-modified Sgarbossa Criteria
- Sodium channel blockade
- Spodick's sign
- Spontaneous change from aberrant conduction
- Spontaneous reperfusion
- Stent
- Strain pattern
- Stroke
- Subendocardial ischemia
- Subtle ST changes
- Sudden cardiac death
- Supernormal conduction
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- T Wave Inversion
- T Wave inversions
- Tachycardia
- Takotsubo
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
- Teaching resources
- Teaching series
- Teaching tips
- Technical error
- Torsades de Pointes
- Transcutaneous Pacemaker
- Tri-fascicular block
- Tricyclic antidepressant overdose
- Trifascicular block
- Triple vessel disease
- Type 2 M.I.
- Type B aberration
- Type I AV block
- Type II S-A block
- V4 Right
- VENTRICULAR TACHYKARDIA
- VPB
- Vagotonic A-V block
- Variable conduction
- Ventricular aberration
- Ventricular aneurysm
- Ventricular bigeminy
- Ventricular capture beat
- Ventricular conduction delay
- Ventricular escape beat
- Ventricular escape rhythm
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Ventricular fibrillation; V Fib
- Ventricular fusion beat
- Ventricular parasystole
- Ventricular premature beat
- Ventricular rhythm
- Ventricular standstill
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Ventriculogram
- Ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia
- W-P-W
- WCT
- WPW
- Wenckebach
- Wenckebach Conduction
- Wenckebach periodicity
- Wenckebach phenomenon
- Wide QRS
- Wide QRS complex
- Wide complex rhythm
- Wide complex tachycardia
- Wide-complex rhythm
- Wide-complex tachycardia
- Wolff-Parkinson-White
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
- Wrong machine interpretation
- Young patient ECG
- Z-fold pattern
- atrial and bi-ventricular
- de Winter T Waves
Dawn’s Classes
ECG Guru Ads - Products and Services of Interest to our Members
If you would like to place ads for products or services of interest to our readers, please contact us at [email protected]
ECG HISTORY: ECG was first put into clinical use in the early 1900s. In 1909, it helped diagnose an arrhythmia. A year later, indications of a heart attack were noted.
-
All our content is FREE & COPYRIGHT FREE for non-commercial use
Please be courteous and leave any watermark or author attribution on content you reproduce.
Recent blog posts
- PACS WITH ABERRANT CONDUCTION
- HOLTER ECG: FAST VT, ATP, ICD SHOCK
- AIVR
- COMPLETE AV BLOCK
- HIGH GRADE AVB
- JUNCTIONAL ESCAPE RHYTM
- POLYMORPHIC VT
- SGARBOSSA CRITERIA
- CONCEALED CONDUCTION
- CONCEALED CONDUCTION AND VENTRICULOPHASIC SINUS ARRHYTHMIA
- PAROXYSMAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
- 2nd Degree Sino-atrial Exit Block, Mobitz Type II
- SICK-SINUS-SYNDROME
- Smartwatch Rhythm Strip
- NON-CONDUCTED PAC



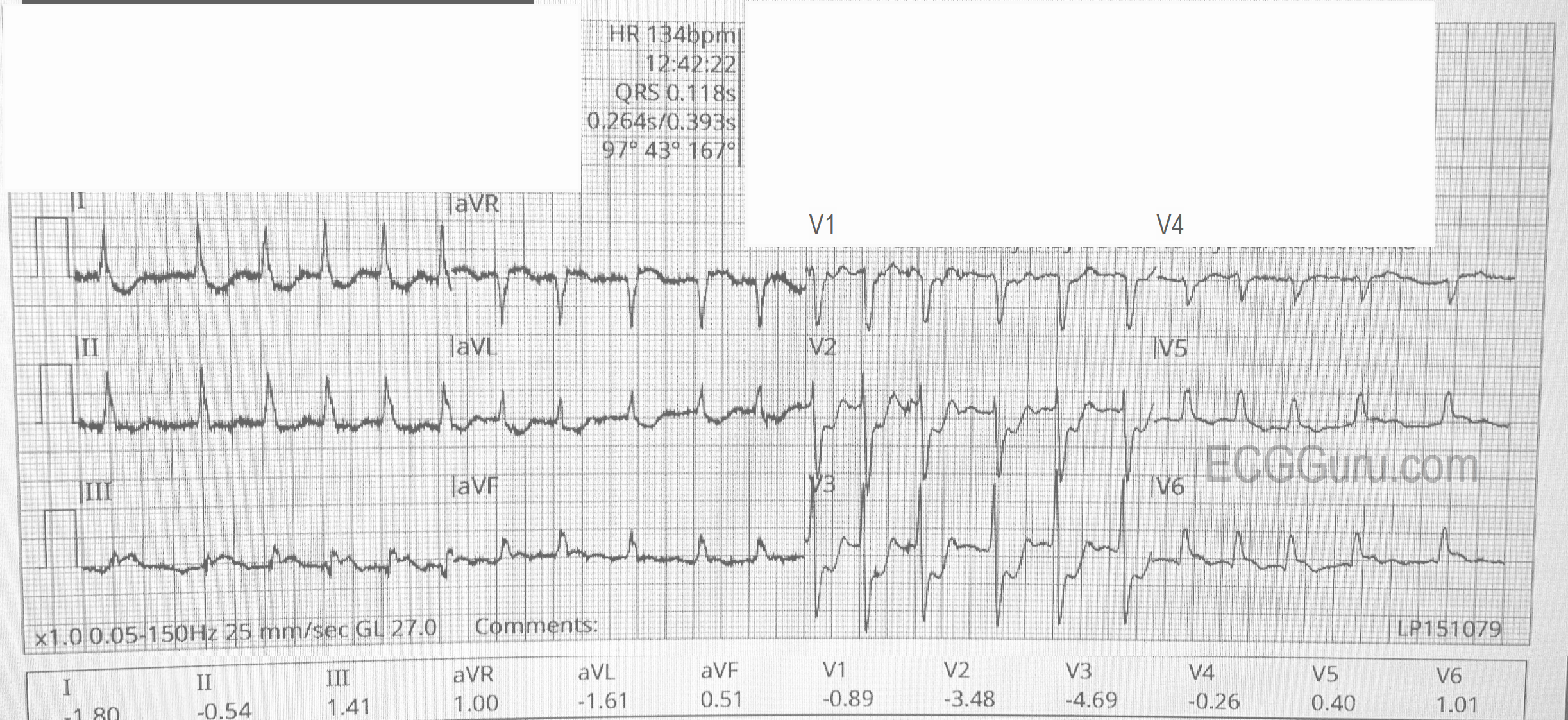
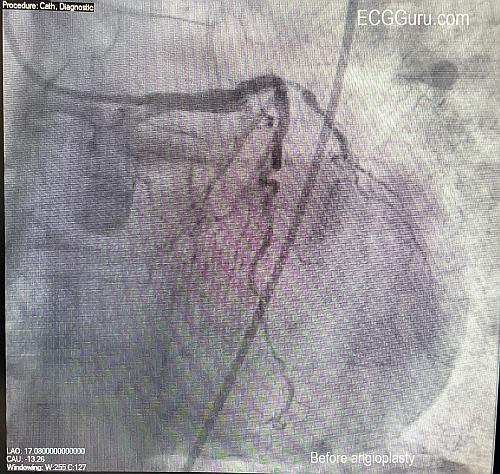
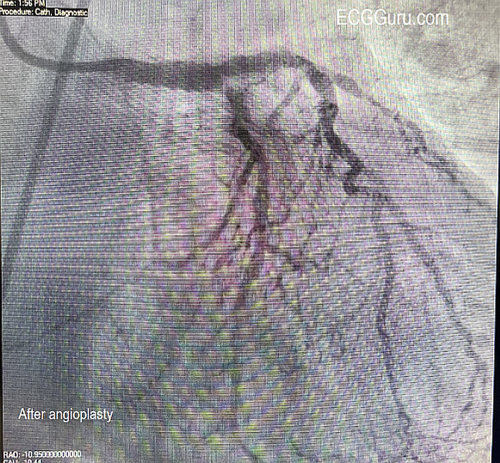

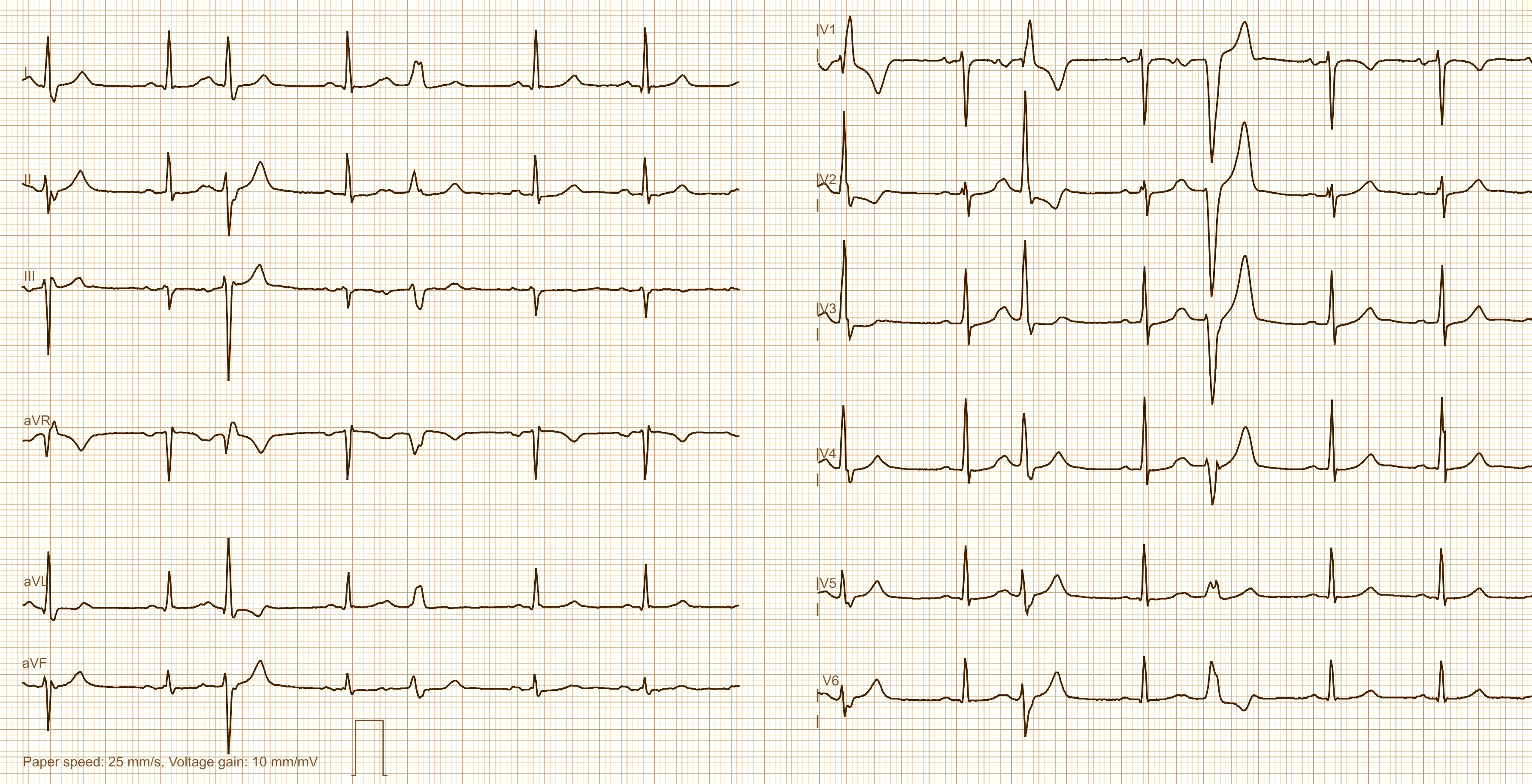
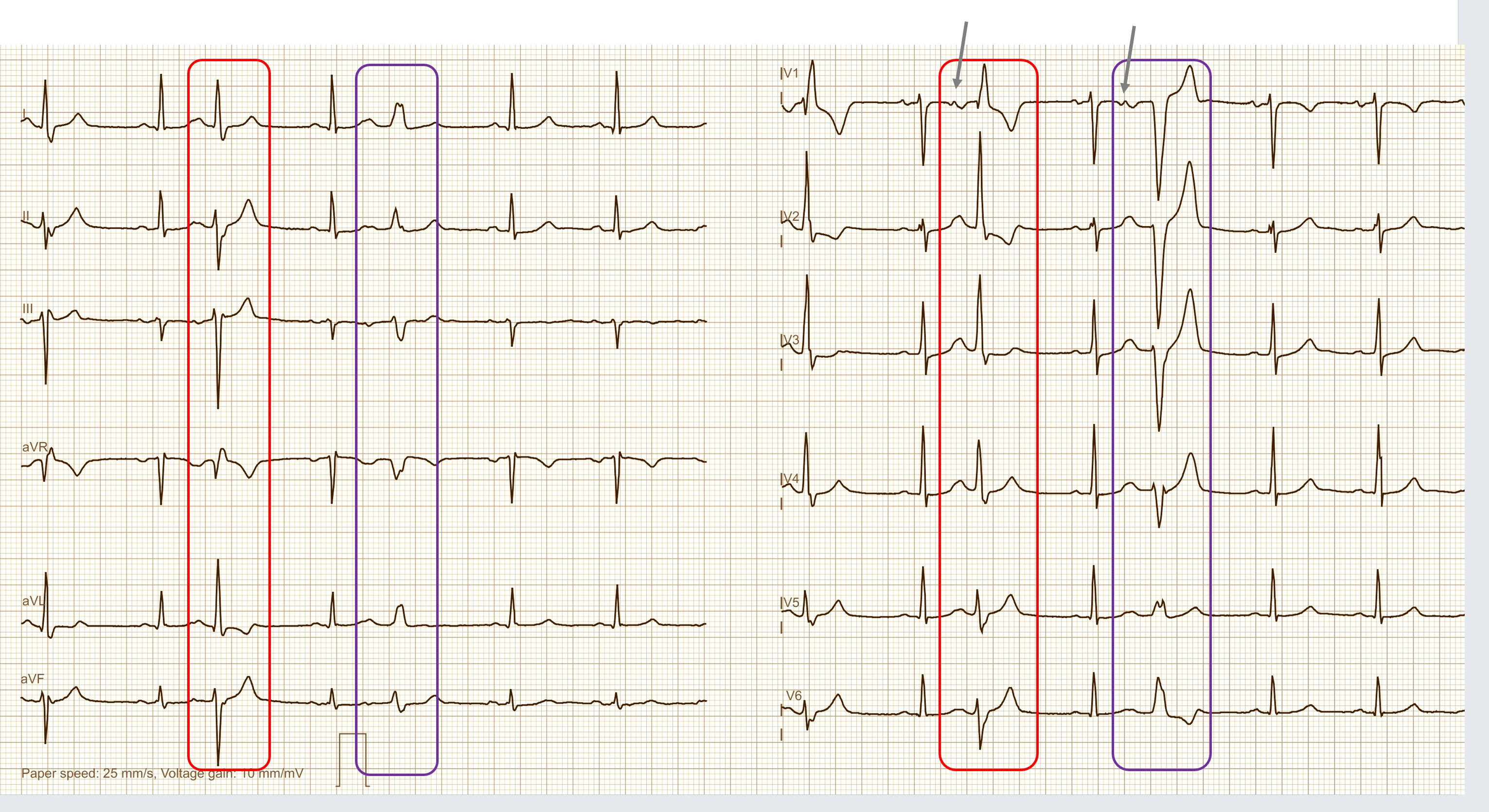
 Today's expert is Dr. Jerry W. Jones, MD
Today's expert is Dr. Jerry W. Jones, MD