Submitted by Dawn on Sat, 02/21/2015 - 17:22
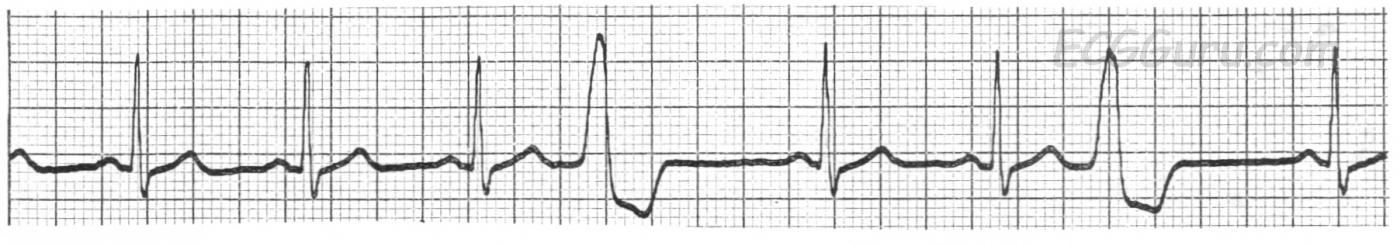
This ECG shows an underlying rhythm of normal sinus rhythm at a rate of 80 / min. There are two premature ventricular contractions (PVCs). The sinus rhythm actually continues uninterrupted, causing a “compensatory pause”. If you march out the P waves, you may even see hints of the hidden P waves in the ST segments of the PVCs. The P waves that occur in the ST segments of the PVCs land in the refractory period of the ventricles, and so are unable to continue into the ventricles and cause a QRS.
It is also permissible to call these beats “ventricular premature beats (VPBs)” or “ventricular premature complexes (VPCs)”.
Rate this content:
All our content is FREE & COPYRIGHT FREE for non-commercial use
Please be courteous and leave any watermark or author attribution on content you reproduce.