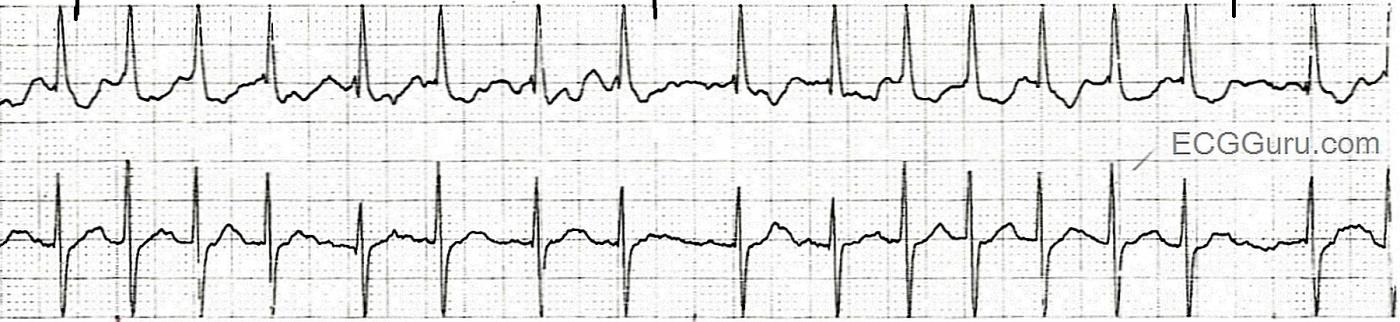
This rhythm strip is recorded in two simultaneous leads, which is always preferable to one single lead. It is a good example of atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response. Atrial fib that has not been treated will usually have a rapid ventricular rate. This reflects the ability of the AV node to conduct a tachycardia, within limits. The natural slow conduction of the AV node allows it to act as a "filter", preventing the huge numbers of impulses generated by the atrial fibrillation from reaching the ventricles. In this case, about 140 beats per minute are able to make it through the AV node into the ventricles. In some patients, preexisting cardiac conditions such as valve insufficiency or CHF may make this rate dangerous for the patient. The rate may lower cardiac output in some people, and this must be considered in light of the fact that the loss of P waves in atrial fib also lowers cardiac output significantly.
All our content is FREE & COPYRIGHT FREE for non-commercial use
Please be courteous and leave any watermark or author attribution on content you reproduce.


Comments
What Happens to Cardiac Output with Rapid AFib? (ie, acute HF)
Ken Grauer, MD www.kg-ekgpress.com [email protected]