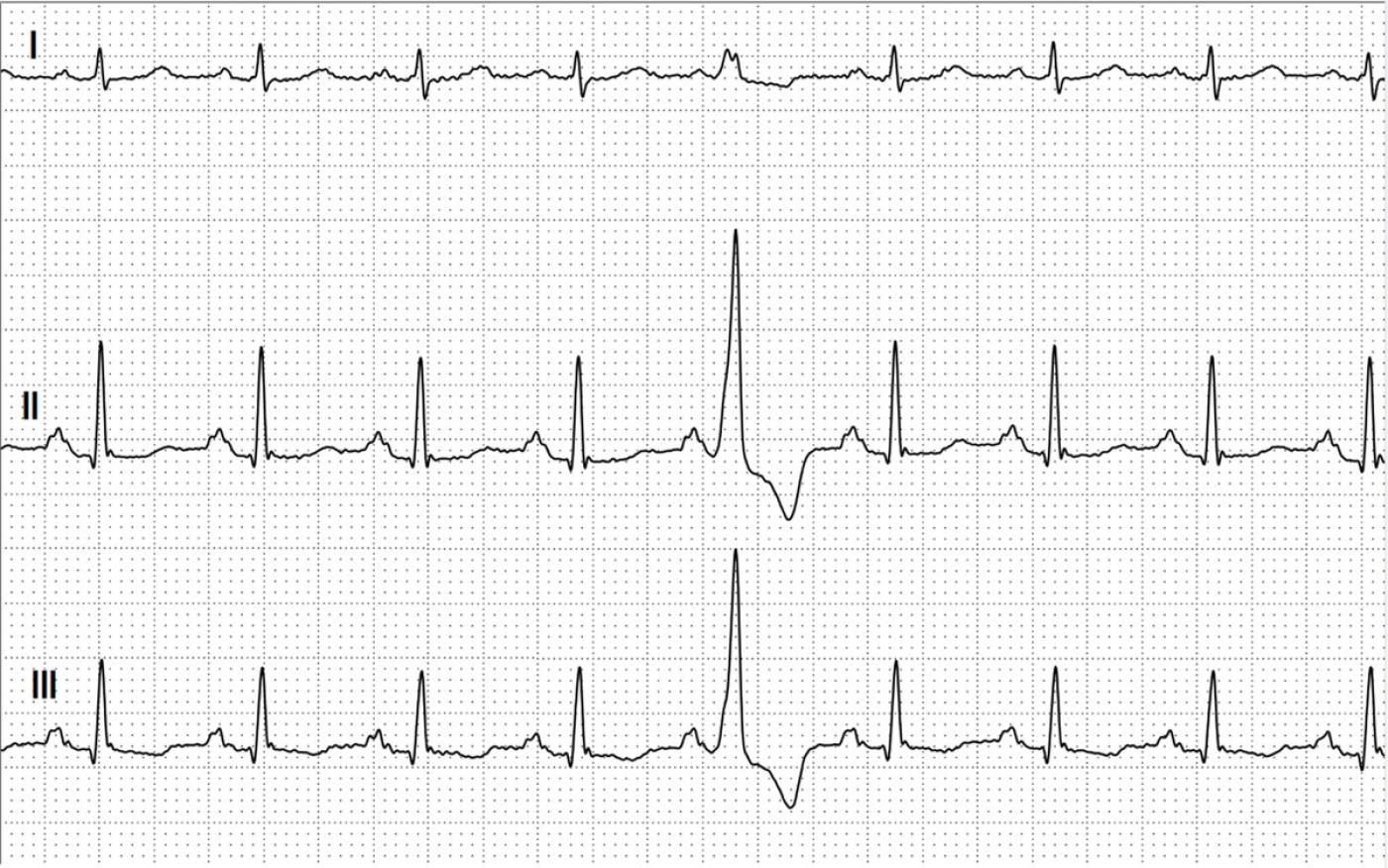
The answer to the question is relatively simple. A premature atrial contraction (PAC) is usually characterized by the occurrence of a premature P wave. If the premature P wave is conducted, it is followed by a premature QRS complex. A premature VENTRICULAR contraction (PVC) is a premature beat from the ventricles with a wide QRS complex. A PVC will not have a P wave ASSOCIATED with it. There may be NO P wave before the QRS, or there may be an UNRELATED P wave present. The sinus P wave may be present if the PVC occurs just after the P, but before a normal QRS can result. This is illustrated here. In this case, the sinus P is not premature, but the wide QRS is. Sinus P waves can also be hidden in the QRS complex of the PVC, or found after the PVC. This is because the sinus P wave finds the atria recovered (repolarized) from the previous beat, while the ventricles are not. In this illustration, we have a premature wide QRS complex (red circles), but P waves that are NOT premature (black circles) and the "apparent" PQ time appears shortened compared to the sinus rhythm. Thus, a PVC is present here.
-
- Dr A Röschl's blog
- Log in or register to post comments
All our content is FREE & COPYRIGHT FREE for non-commercial use
Please be courteous and leave any watermark or author attribution on content you reproduce.